OUTLINE OF PROGRAM
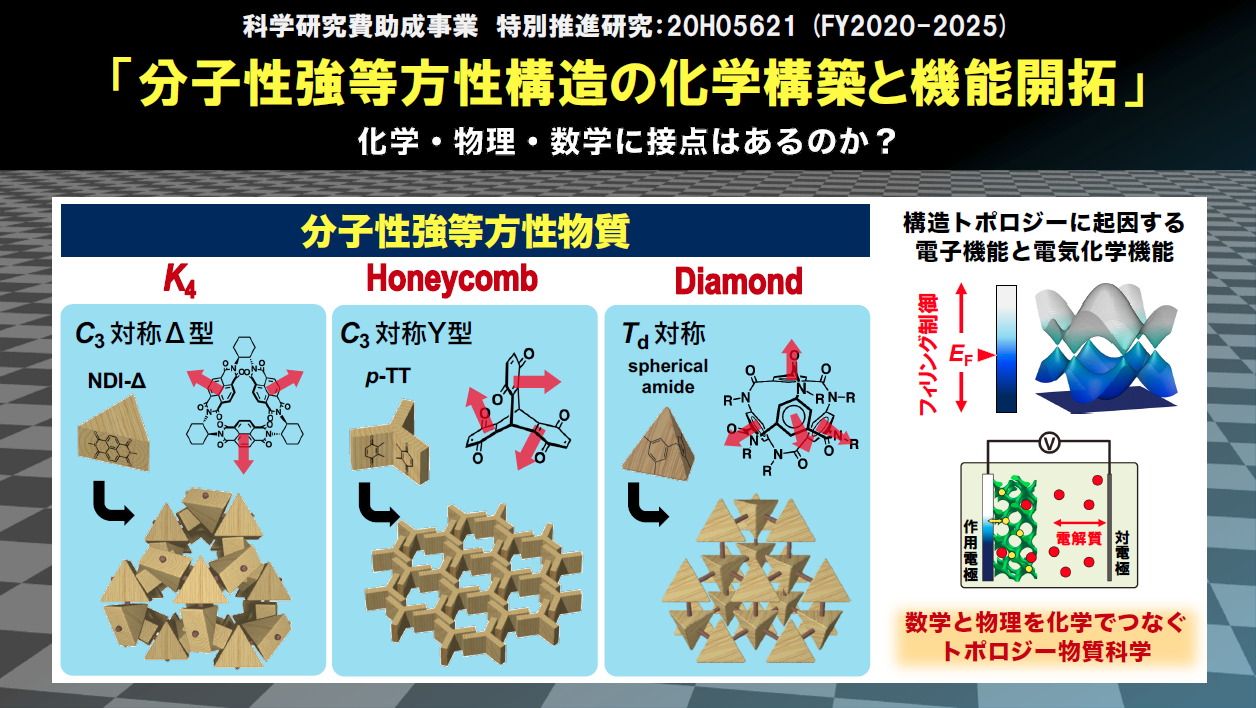
Recently, the graph theory recently has predicted the K4 structure as a new carbon allotrope. It is mathematically demonstrated that only the three lattices, namely honeycomb, diamond and K4, which are lattices of the carbon allotropes, exhibit the property of “strong isotropy”. It is notable that the band structures of the three carbon allotropes include exotic band dispersions, which are characterized as Dirac cone, Dirac nodal line, and triplet Dirac cone, respectively. Therefore, if the Fermi levels can be freely controlled in them, Dirac fermion systems would be newly constructed. However, it is hard to realize this idea in the carbon allotropes, so that we propose to make molecular mimics of the carbon allotropes, and then to carry out the band filling controls, taking advantage of their porous structures and redox activities. The purpose of this project is to exploit the electronic/spin functions originating from the topology of strong isotropic lattices, developing electrochemical band-filling control. We also elucidate the solid-state electrochemical functions, derived from the synergetic effects between electron and ion transport in the molecule-based strong isotropic lattices.
近年、グラフ理論によって炭素の新しい同素体「K4炭素」が提案されました。このK4炭素は、炭素同素体としてよく知られているダイヤモンド、グラフェンとともに、幾何学において「強等方性」と呼ばれる性質をもっています。 これらは、その構造トポロジーを反映した極めて特異なバンド構造を有しており、もしそのフェルミ準位を自由制御できればDirac電子系を人工構築できるはずです。しかしながら、K4炭素の合成に成功例はなく、フェルミ準位の自由制御は夢のまた夢です。 そこで我々は、炭素同素体の結晶構造、つまり強等方性格子を分子結晶でつくる着想を得ました。このような分子性強等方格子には、炭素同素体にはない巨大内部空間やFlat Band、酸化還元能などの電子機能も期待されます。 本研究では、分子性強等方構造の合理的な構築を達成した上で、電気化学的バンドフィリング制御法を確立し、強等方性トポロジーに起因する多彩な電子・スピン機能を引き出し、電子とイオン輸送の協奏する固体電気化学機能を開拓します。